Because every device can be wireless
Historically limited radio frequencies have been allocated for different applications. Because of technical limitations lower frequencies have been allocated first. Over time technology has developed and higher and higher frequencies have come available. When digital mobile phones came on the market with reasonable prices, frequencies were allocated for the first time to several operators to provide the same service (voice). There were more potential operators willing to buy frequency licenses than available frequency blocks. When this happened at 90’s frequencies were tied to certain technologies so auctioning was extremely easy to organize. Today mobile network frequency prices have risen to billions of Euros.
Today mobile broadband dominates the frequency market and is frequency limited, there is more demand than capacity in mobile networks. This is acceptable for best effort applications where we can use buffering to overcome capacity fluctuations. Best effort from a mobile broadband network is good enough for many such services that have previously used their own frequency for example radio/TV broadcasts, meter reading, turning machines on/off etc. These and many more use cases use mobile broadband networks but demand constantly more and more frequency resources.
Best effort networks won’t serve all existing needs that are served by application specific frequencies. Today and in the future, there are more and more devices that would require their own frequency allocations and it is not possible to find good frequency for all these applications. Quality of Service (QoS) technologies have been developed to be able to provide predictable service levels for those applications that require Service Level Agreements (SLA). Target is that by using QoS technologies we can get rid of application specific frequencies and use those frequencies to serve several applications. This is expected to improve frequency utilization rate and provide lower cost and more flexibility for SLA sensitive applications.
Old mobile broadband model does not work to serve SLA applications. There are two different approaches developed to enable usage of mobile broadband network frequencies for SLA dependent applications, Network Slicing in public networks and non-public networks. Both technologies are most likely needed to come up with a good solution for all. Network Slicing in public networks provides wide area coverage but it is always a compromise between best of users and Network Slice users. Non public networks require strict frequency control and own Network hardware and software investment.
Non-public networks require a frequency coordination that ensures interference free RF environment for the network. Frequency licenses can be for a long or short period of time. Long licenses can be for example a concert hall and short licence period an orchestra performing in several concert halls. It is also possible to have auctions for different frequencies for a smaller than today geographical area. Frequency licenses can also be tied to the property location at least for some frequencies.
Using the same frequency for several purposes it is expected to increase frequency utilization rate. Using the same network technology also drives down equipment cost (User Equipment and Network) that will make it possible to use the network for even more applications. Higher volumes will accelerate technology development.
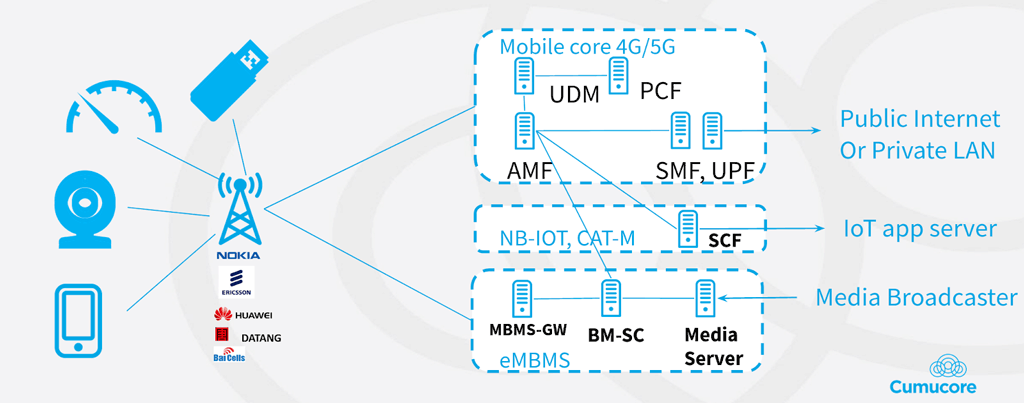
Want to know Cumucore solution? Software to create mobile private network
Wireless options comparison
There are three options to connect devices wirelessly. These options have different pros and cons. Selection of what option to be used should be based on the need of the project.
-
Using existing Wifi infrastructure
WiFi system has wireless routers that are connected to access points and controllers. Access points are typically connected by cable to controller but there can also be mesh network topology. In a mesh network only one access point is connected to the controller. Access to the network is managed by passwords. WiFi network data can stay local or can be managed from the public cloud.
Using WiFi infrastructure is a fairly low-cost investment because typically the basic infrastructure exists. Integrating WiFi networks to be part of other IT networks is easy.
WiFi has a limited output power leading to limited coverage. This means that it does not fit well to cover large areas. WiFi networks use unlicensed frequency so from time to time there are connectivity problems related to air interface interference. Connectivity problems are visible to the user the way that there is not enough capacity and/or delay in the system increases. Typically, WiFi networks are used for other traffic as well so from time to time there might be congestion issues. WiFi standards are developing quickly meaning leading to a risk that WiFi systems need to be upgraded every five years or so.
-
Using existing commercial mobile network
Commercial mobile network needs only a wireless router with a SIM card to connect to the device. In commercial networks data will always leave premises.
Commercial mobile networks are available practically everywhere. Commercial mobile networks are using licensed frequencies, so air interface interference is not a problem. Using commercial mobile networks requires an agreement with a mobile operator and SIM cards. SIM cards are charged monthly so there is a monthly recurring cost. Mobile standards are backward compatible meaning that lifetime of devices are long typically decades.
Commercial mobile networks won’t provide good coverage to everywhere and it is unlikely that mobile operators are willing to fine tune their network based on one customer need. Mobile networks are best effort networks and time to time they suffer congestion. In large implementations physical SIM cards will lead to lock in to one mobile operator. There are new features like eSIM and Network Slicing coming in but at the moment (December 2020) they are not viable solutions to be used for connecting Quuppa locators.
-
Private mobile network
Using a private mobile network means that there is a dedicated frequency license for the area network is built. To build a network there is a need for a mobile core, basestation(s) and wireless router with a SIM card. Private mobile network can run stand-alone, meaning data is local or it can be connected to the Internet.
The benefit of licensed frequency is that there is no air interface interference. Private networks use exactly the same standards than commercial networks, so all same devices are available for private mobile networks than commercial networks. Private mobile networks can be optimized for a very short delay in the network (<1ms). Private network is fully managed by the user so it can be dimensioned so that there is no risk of congestion. Coverage of private networks can be built as needed and because output power limits are high the required number of basestations is low. The cost of running a private network is similar to running a WiFi network and the required skill set is the same. There are new features coming available to facilitate integration between private mobile networks and other IT infrastructure. These features are called 5GLAN and Time Sensitive Network (TSN).
There is a cost related to frequency license and they are not available in every country to be used for private mobile networks. Wireless routers need a SIM card that is a private network specific.
Private Neworks, what are the benefits in details
Control over network
Private mobile network provides you total control of the network. You can define who can access your network, when they can access, what kind of Quality of Experience they have, what kind of coverage your network has and how much capacity is available. There are no compromises needed because of Internet neutrality or equal service requirements.
Traditional public mobile networks are designed for best effort usage, they provide equal service for different applications, service level is depending on the load of the network. In public mobile network coverage is a compromise between cost and service level. Network dimensioning is done for an average load, compromising customer experience during peak hours. Public mobile network is not a suitable solution for mission critical applications.
Private network service is always designed for a certain customer per location. This means that there are no compromises needed. Network is designed for reliability without a huge cost impact. High reliability is achieved because there is full control of subscribers in the network, low cost is achieved because of modern software technology.
Replacing fixed Ethernetwork in the enterprise and factories can be done when using private mobile networks. Private mobile networks are easier to use than fixed networks and can be pre configured for different situations and for example applications can be prioritized in the case of network failure and other extraordinary situations. Network capacity can be designed to meet the need in any circumstance.
Interference control by frequency coordination
Private Networks use regulated frequency so there are no issues with interference. The network with regulated frequency has a constant network capacity without impact from random users in the premises. Clean frequency is a base for reliable and predictable service level.
Frequency policies vary between countries, but there are 5G frequencies available around the world. Private networks can work in static frequency allocation or temporary frequency license.
Security on premises installation
Private network can be installed as a stand alone network. Stand alone networks means that it does not require connection to the Internet. All data can be stored and processed on the premises. Local data management gives uncompromised control of business critical data and controls operations. Local data operations also enable use cases where applications require millisecond delay
Volume benefits from standards
Private Networks are 3GPP compliant. Work in 3GPP is going on all the time utilizing the best information network resources in the world. Private networks will have improvements over time and they will also meet the future requirements. Global cooperation means not only state of art technology but also lower cost. There are roughly 10 billion 3GPP standard users in the world. Cost of wireless communication has decreased at the same time when performance has increased. Going forward with 3GPP technology is a future proof solution.
5G is not only a new air interface but new network architecture. 5G is based on fully virtualized network functions that means that there is no more need for expensive proprietary hardware and difficult upgrading processes. In 5G it is easy to add new network features and upgrade existing features to meet new requirements.
Cumucore’s private network implementation
Use case optimized networks
Fully virtualized 4G and 5G core that is based on containers. Cumucore’s SW architecture scales down very well and makes it feasible to deliver even networks with only one base station. This innovation makes it possible for every business to benefit from the 5G network development. Running your own mobile network is now possible for everybody!
Cumucore’s solution is tailored to meet different vertical industry needs. Cumucore can deliver an end to end solution using commercially available end devices and eNB/gNB from Nokia. Cumucore is 3GPP compliant so any eNB/gNB vendor will work with. Cumucore supports base stations from femtos to macros.
Affordable
Cumucore 4G/5G core runs on virtualized environment. The virtualized environment can be installed on any commercial Linux computer platform. This is not only very cost efficient but also very scalable. Cumucore core can be scaled up and down based on the current need of network resources. The same computer platform can also host resources for local applications. This reduces application latency to minimum and also can help to reduce transmission needed to the Cloud.
Easy to use
Traditionally mobile networks have been difficult to use with several network elements that require specially trained personnel. Cumucore has been able to develop a simple user interface that is controlling the whole network. The Cumucore network has all the functions that 3GPP has specified, we have developed a “skin” on top of them to deliver interfaces that you can use with regular IT skills.
Using Cumucore does not require any special mobile networking skills. Needed base stations and SIM/eSIM cards will be delivered preconfigured for immediate activation. You can install Cumucore 4G/5G core on your local environment and configure the network by yourself. Network can run as a stand alone network, as a part of fixed LAN infrastructure or connected to the Internet as a regular mobile network. Network can run on a regular 19” server but in the smallest configuration it can run on a very small box that can be carried around with you wherever you might need a powerful mobile network.
Do you need a non-public network? Cumucore’s Software connect your company
The most important questions about PRIVATE NETWORKS:
- Why should companies get a private network?
Companies have more and more needs to automate further their processes. To automate processes companies need reliable and wide coverage area mobile networks. - Why Private Networks are Essential to Drive Enterprise Digital Transformation?
To drive digital transformation further we need to allow devices to move around and still be connected to enterprice infrastructure. - The best 5 benefits of private networks for enterprises:
Higher security, because data won’t leave premises, low latency because data processing in on premises, high reliability because enterprice has own frequency and total control who can access the network, flexibility, because network can be tailored to meet all requirements and lower cost because there are less cabling required. - What industry challenges and opportunities needs a MPN to resolve it?
Allow flexibility to change manufacturing process and still utilize existing IT infrastructure. - Can Ethernet cable and mobile coexists on private networks?
Yes they can, thanks to 5GLAN feature. - Principal Enterprise private network advantages and disadvantages.
Advantage is security and low latency. Disadvantage is requirement to have a frequency licence and that licence terms in different countries are different. - What is enterprise private network?
Private network is such where network resources are not shared between different entities. - Common network issues that a MPN can be better:
Allow outdoor areas to be connected to existing IT infrastructure easily and provide interference free mobile connectivity.






Pingback: Cumucore has installed its 5G core successfully on RedHat OpenShift - Cumucore